Congratulations to Mr. Yuting AN (first author) and Mr. Zhuolun NIU (second author), Ph.D. students of Professor Chun CHEN, for winning the 2022 Best Paper Award for a Young Author from journal Building and Environment.
The journal received about 5500 submissions in 2022 and only four best papers and two best papers for a young author are selected.
Title: Smart control of window and air cleaner for mitigating indoor PM2.5 with reduced energy consumption based on deep reinforcement learning
Abstract:
For naturally ventilated apartments equipped with air cleaners, it is essential to develop a controller that simultaneously controls the operation of a window and the air cleaner in order to mitigate indoor PM2.5 (particulate matter with aerodynamic diameter less than 2.5 μm) pollution with less energy consumption by the air cleaner. This investigation first employed the deep reinforcement learning approach to train a smart controller that minimizes the total economic loss due to PM2.5-related health risks and air cleaner energy consumption. The controller was trained offline in a virtual apartment constructed on the basis of a particle dynamics model with typical building parameters. The inputs required for the controller were the real-time indoor and outdoor PM2.5 concentrations, which could be measured by low-cost sensors. To test the trained deep Q-network (DQN) controller, a series of experiments were conducted in two laboratory chambers. Both the indoor PM2.5 concentrations and the operating time of the air cleaner were compared between the trained DQN controller and different benchmark controllers with various outdoor PM2.5 levels under different chamber conditions, in order to assess the controller performance. The trained DQN controller outperformed the benchmark controllers in reducing the total economic loss due to indoor PM2.5-related health risks and air cleaner energy consumption by 2.4% to 43.7% for all 18 cases. Although the DQN controller was trained offline in a virtual apartment with typical building parameters, its performance was robust in the chamber experiments even when the parameters were very different from the typical values.
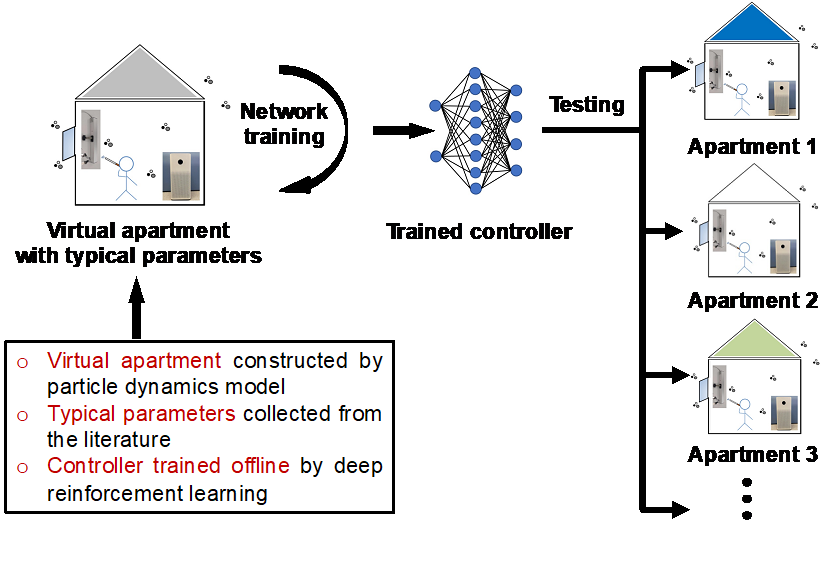
General framework of the particle dynamics based deep reinforcement learning approach.
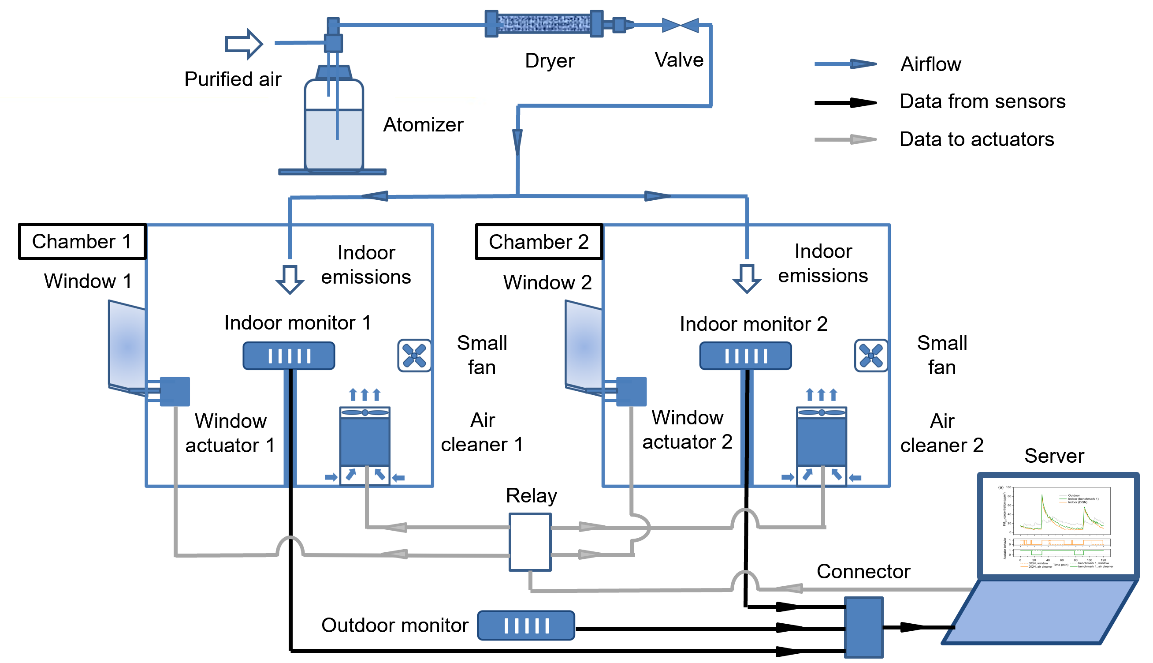
Schematic of the experimental setup to test and compare the performance of DQN and benchmark controller.
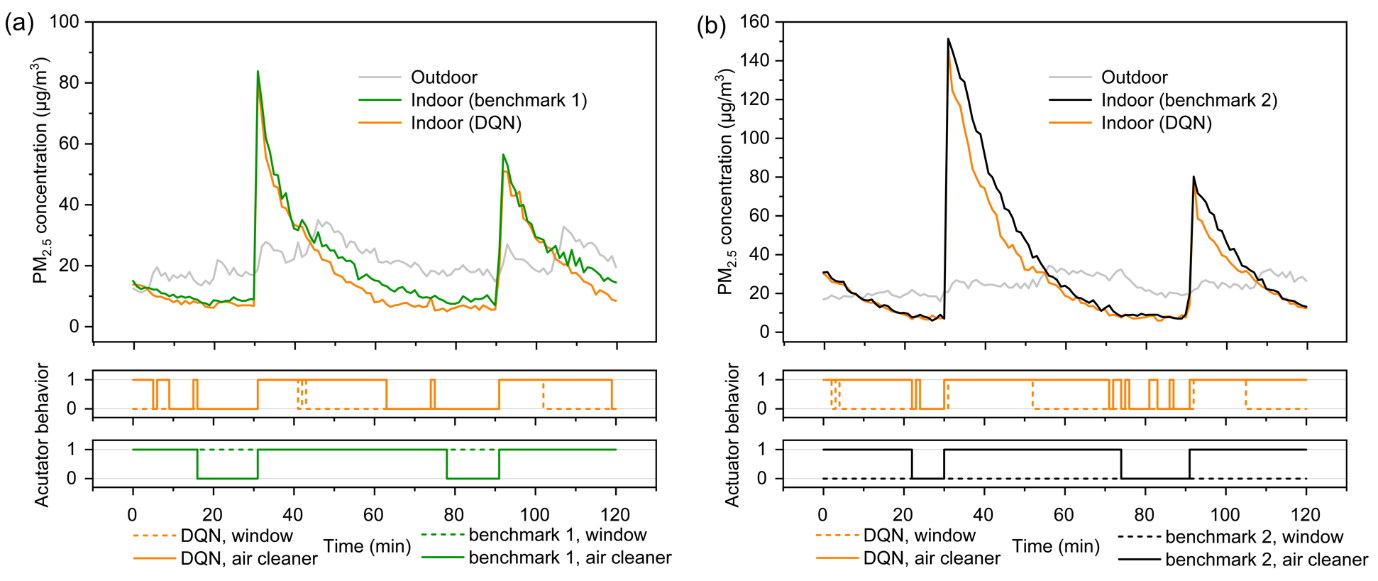
Comparison of the indoor PM2.5 concentrations and actions of the air cleaner and window actuator between the DQN controller and (a) benchmark controller 1 (window opened) and (b) benchmark controller 2 (window closed) for chamber condition 2 (chamber parameters close to typical values) when the outdoor PM2.5 level was low.
Mr. Yuting AN (first author)
The full text can be found at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2022.109583.