 Programme Features
Programme FeaturesInterdisciplinary by design, the Programme strongly leverages the relevant expertise and capabilities offered by CUHK as a comprehensive university. In addition to the fundamental knowledge of energy principles, technologies and systems, the Programme features a number of required and core elective courses co-designed with the Earth System Science Programme, and a host of elective courses from the Environmental Science Programme and the Department of Geography and Resource Management, for a broader and in-depth education on the environmental impact of pollution in urban settings.
Students are able to pursue any one of the three streams of study according to their personal and career interests: the Sustainable Energy Technology stream for enhanced coverage of renewable energy generation, system design, storage, distribution and management; the Green Building Technology stream for fundamental knowledge of environmental performance assessment and energy management of urban buildings; and the Environmental Engineering stream for principles of natural and built environments, and air pollution monitoring and control challenges.
The Programme also includes courses in technical communications, engineering ethics, design application and final year projects to enhance students’ training as professional practitioners. Students are able to participate in and benefit from the many campus and community projects and research topics offered by the university-based institutes and units on environmental studies and sustainable development. They can also enjoy ample opportunities for summer internships, work-study programmes and international exchanges.
 Admission
AdmissionJUPAS Code: JS4462
Admission is based on the Best 5 HKDSE subject results with subject weighting. For details of minimum admission requirement and subject weighting, please refer to the table below. This is applicable to HKDSE applicants for 2024-25 onwards.
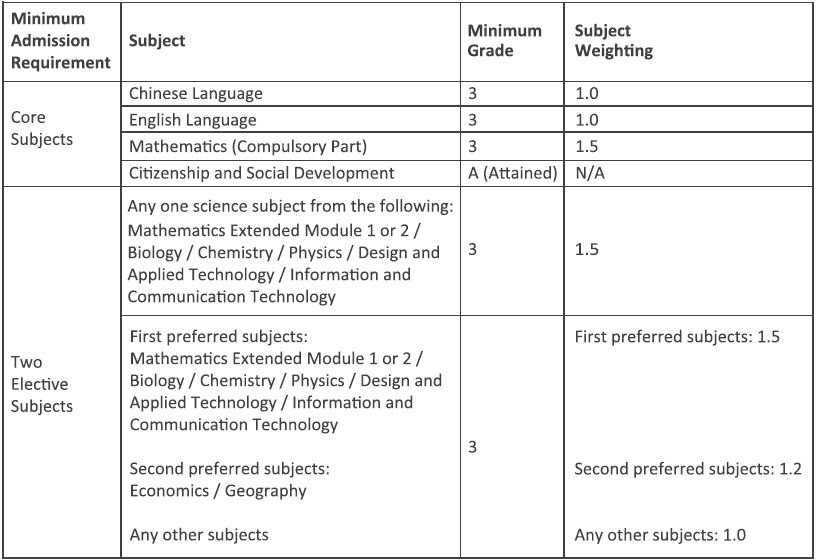
The programme accepts “Attained with Distinction I or II” in Applied Learning subjects as extra elective subject for awarding bonus points. Please refer to https://www.cuhk.edu.hk/adm/jupas/ApL for details.
Interview for JUPAS applicants will be arranged on a selective basis.
Local Entrants
- Non-JUPAS (Local) Admission Scheme*: Local students who possess post-secondary qualifications such as International Baccalaureate, GCE A-Level, SAT, Higher Diploma and Associate Degree can apply for admission to the programme. Click here for details.
- Senior-year Intake for Sub-degree Holders: Local students with excellent results in their Associate Degree or Higher Diploma study can apply for admission to the senior year of the programme. Click here for details.
International Entrants*
- Students requiring a student visa to study in Hong Kong can apply for admission to the programme by using post-secondary qualification such as International Baccalaureate, GCE A-Level and SAT. Click here for details.
Mainland Entrants
- Click here for details
 4-year Curriculum (Applicable for students admitted in 2024-25)
4-year Curriculum (Applicable for students admitted in 2024-25)
123 units
Free Electives
9 units
University Core Requirements
39 units
Major Programme Requirements
(Breakdown as follows)
75 units
The effort of securing more sustainable, reliable, and affordable energy supplies is among the most challenges faced in this century. This course focuses on scientific and engineering fundamentals of renewable energy resources and conversion technologies. The subject-specific lectures will be provided in more depth to cover these topics: global energy sources, thermodynamics for renewable energy, solar energy, wind energy, hydro power, bioenergy, geothermal, fuel cell, and design, modeling and analysis of energy systems.
This course aims to provide students with an introduction to economic principles that pertain to energy and environment. The objective is to apply economics to particular issues of energy markets, energy planning and demand management, government regulations and policies, environmental impact and conservation, local pollution control, and new technologies.
The course will cover fundamental concepts in economics including utility and preference, supply and demand functions, cost-benefit analysis and market equilibrium, project evaluation and management, externality, and game theory. Through this course, the students will understand the interactions and possible externalities between energy, environment, economy, and sustainability. The students will acquire skills in conducting energy and carbon auditing, and also learn how to analyze the effects of government policies and regulations on energy demand and supply, prices, carbon emissions, to name a few.
This course introduces the heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning (HVAC) systems for buildings. The contents include psychrometrics, air-handling process, zones, single-zone system, constant air volume (CAV) systems, variable air volume (VAV) systems, hydronic system and architecture, central plant, thermal comfort, ventilation and indoor air quality.
The course combines activities designed to develop employability with the knowledge and skills gained through attending workshops or seminars. Successful completion of the course will provide students with the employability skills required for transition to the world of work. Students who have attended certain industrial and professional workshops or seminars required by the EEEN programme may be able to count these towards the course.
This course introduces fundamentals of materials including atomic bonding; crystal structures, defects; mechanical properties of materials, phase diagram; overview of metals, alloys, ceramics, polymers, semiconductors and composites; electrical, optical, magnetic, and thermal properties of materials; materials selection and design considerations for engineering technologies. Applications of materials to energy and environmental engineering, mechanical engineering, medical engineering, and others will be discussed.
This is a multidisciplinary course introducing the fundamental physical, chemical and biological principles necessary for understanding the natural and built environments, with an emphasis on reliable water and food supplies, pollution mitigation, waste management, energy resources, climate change, and sustainable development. Examples of engineering solutions to tackle some of these resource and environmental issues are presented. Field trips are included to illustrate interesting case studies. Topics include: conservation principles for mass, energy and momentum in the environmental systems; basic environmental chemistry, hydrology and ecology; risk assessment; and basic principles of water resource engineering, solid waste treatment, noise pollution, air pollution control, climate change adaptation and mitigation, and the interplay between energy consumption and the environment.
This is an introductory course on electric circuits. The main content include basic circuit laws and theorems, methods of circuit analysis, operational amplifier circuits, and the concept of linear feedback system. The basic concepts of AC circuits, including impedance, phasors, sinusoids and frequency response, will be taught. The course will also cover the fundamentals of electrical power systems, including transient analysis, three-phase circuits, inductors and transformers, and basic electromechanical principles. This course includes mandatory laboratory modules.
This is an introductory course to power electronics. Semiconductor power switches and the principles and methods of switched-mode power conversion are introduced first. Important concepts needed in power electronics are reviewed. The course then goes to analyze and design four categories of switched-mode power converters: AC-DC, DC-DC, DC-AC and AC-AC, their different modes of operations, and their applications, for instance, in DC power supplies, electric vehicle chargers and clean energy generation systems. Control circuits employing negative feedback for switched-mode DC-DC converters are introduced and analyzed, and their design methods are illustrated.
This course will cover fundamental topics in thermodynamics including basic concepts, heat and work, pure substance, ideal gas, first law and second law of thermodynamics, entropy, gas and vapor power cycles, and refrigeration cycles.
This course introduces basic and fundamental knowledge in technology, engineering, and their impacts on human society. Important and various aspects of engineering will be introduced, like engineering design and innovation, engineering project management, and intellectual property. Student have opportunities to participate some field study to have a better understanding of engineering design, innovation, and industrial manufacturing in practice. This course also provides several seminars given by real engineers with topics on current engineering issues, career decision-making strategies, and opinions such as internships and life-long study.
This course covers important topics in fluid mechanics. It will introduce the nature of fluids; pressure, hydrostatics, and buoyancy; integral and differential equations of fluid flows; conservation of mass, momentum, and energy; basic mass transfer; inviscid flow, viscous-dominated flows; Navier-Stokes equation; dimensional analysis; internal and external flows, boundary layers, and lift and drag on objects.
This course will cover fundamental topics in heat transfer including physical origins of three heat transfer modes and their rate equations, heat diffusion equation, boundary and initial conditions, steady-state and transient conduction, numerical methods, boundary layer equation, external and internal forced convection, free convection, and thermal radiation.
The course is designed to provide students with an opportunity to carry out, under the supervision of an academic staff, an independent project with research elements in engineering.
The course is designed to provide students with an opportunity to carry out, under the supervision of an academic staff, an independent project with research elements in engineering.
Biofuel, namely fuel produced through chemical engineering processes of biomass, represents a major alternative and sustainable source of energy. The course covers review of organic chemistry and physical chemistry; structures and combustion energy of fuel molecules; related biochemistry and enzymology; biochemical conversion processes; ethanol production from carbohydrate-based biomass; biodiesel production from lipid-based biomass; hydrogen and methane production from organic and waste products; fermentation and alkane production; chemical engineering processes of biofuel production; biofuel economics, policies, and research and development; field trip to bioenergy farm. A guest lecture from a practitioner on biofuel production industry is scheduled. Students are required to run experiments for a project and to design their own solutions to solve problems met in biofuel industry.
In this course, we will discuss kinetic energy harvesting devices and systems, from basic mechanisms to applications. The first half semester of this course will start with talking about the fundaments of kinetic energy harvesting, including mechanisms of electromagnetic, piezoelectric, triboelectric, electrostatic, and others. And then it will cover basic device designs and energy transfer; physics and circuit models; electromechanical modeling and analysis; simulation methods and practice; and interfacing circuits. The second half semester will cover the applications of kinetic energy harvesting in various situations, including power plants, wind turbine, vibrations, hydro system, ocean waves, body motions and others, and ends with discussions on kinetic energy harvesting technology in the future. The evaluation will be based on final project, midterm exam, homework, lab report, and participation in class.
This course provides students with knowledge of solar energy and photovoltaic technologies. It covers the following topics: introduction to solar energy technologies, semiconductors for photovoltaics; working principle and performance evaluation of photovoltaic cells (PVs); photovoltaic technologies (crystalline PVs, thin film PVs, and organic and nanostructure based PVs), solar panel system design, cost aspects, and market development and environmental impact of photovoltaic industry.
This course will introduce the basic nuclear physics – elementary quantum theory; nuclear forces; shell structure of the nucleus; alpha, beta, and gamma radioactive decays; nuclear reactions; fission and fusion. In addition, this course will discuss the nuclear power plant design – nuclear power plant layout; reactor dynamics; reactor start up and process control, waste treatment. Risk management – assessment and management of nuclear safety, radiation, exposure and environment, safety assessment will be introduced in this course.
This course describes the fundamental principles, device and system design of energy storage technologies including electrochemical energy storage (batteries, supercapacitors, fuel cells etc.), thermal energy storage (phase change), mechanical energy storage (flywheel and compressed air energy storage), hydrogen storage. The applications of energy storage technologies in supporting renewable energy sources for smart grid, hybrid and all-electric vehicles, and green building applications will be discussed.
This course will introduce electric power system fundamentals, control, and operation. The course will discuss power system components and overview, review of basic circuit elements, AC circuit analysis and phasor representation, complex power, active and reactive power, power factor and power triangle, reactive power compensation, balanced 3-phase system analysis, Yconnection and delta-connection, transformer modelling and analysis, per-unit analysis, transient stability and analysis, voltage stability and control, frequency stability and control, power flow analysis, economic dispatching, optimal power flow problem, power plant planning, smart grid, energy storage system, renewable generation and utilization, and electric vehicle integration.
This is an introductory course on electric power systems and electrical to mechanical energy conversion. Electric power systems have become increasingly important as a way of transmitting and transforming energy in industrial, military and transportation uses. They are also at the heart of alternative energy systems, including wind and solar electric, geothermal and small-scale hydroelectric generation. This course covers fundamentals of energy-handling electric circuits, power electronic circuits such as inverters, and electromechanical apparatus; modeling of magnetic field devices and description of their behavior using appropriate models; analysis of power electric circuits, magnetic circuits, and elements of linear and rotating electric machinery; models of synchronous, induction, and DC machinery; the interconnection of electric power apparatus and operation of power systems.
This course provides both fundamental knowledge of nanomaterials and nanotechnology and advanced topics related to applications. These topics cover basic principles, which include the scaling law, the surface science for nanomaterials, observation and characterization tools for nanomaterials, the nanofabrication techniques, building blocks for nanodevices and systems, etc. In the second half of this course, advanced topics on applying nanomaterials and nanotechnology for applications in mechanical engineering, energy engineering and biomedical engineering will be covered.
This course will cover advanced topics in heat transfer and fluid mechanics including overview of macroscopic theory of heat transfer, microscopic picture of heat carriers and their transport, micro- and nanoscale energy transport in solids, chemical thermodynamics, chemical kinetics, multicomponent and multiphase mixtures, basic principles of computational fluid dynamics, turbulence modeling, and airflow simulation in enclosed environments.
This course introduces the control strategies of the heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning (HVAC) systems, including introduction to building automation, control of CAV systems, VAV systems, chilled water systems, chillers, cooling towers, design and control, control devices and BAS. This course also introduces thermal insulation, heating and cooling load calculations, ventilation and infiltration.
This course emphasizes the intersection between energy consumption and human/corporate/economic activities. The course follows a grid structure in its organisation. The grid’s horizontal lines are about energy consumption, involving electricity use, and direct burning of fuels including combustion engines, boilers, stoves, etc. The vertical lines are about human activities, involving major economic sectors including the industrial, transport, commercial, and residential ones. The intersections between the grid’s horizontal lines and vertical lines are the lecture topics. Each lecture has discussion over three aspects: (1) how energy is utilized; (2) what factors are affecting energy consumption in intensity and in total; and (3) how human behaviour could be changed for energy conservation and pollution control.
This course introduces technologies, strategies as well as management and assessment systems to improve sustainability of buildings in relation to their environmental impacts. Applications such as passive design strategies, energy efficient systems, renewable energy and building information modelling are illustrated for enhancing the building performance and fulfilling green building assessment criteria and related regulations. The course will also enable students to adopt a lifecycle assessment approach to analyze building environmental performances and tackle with concurrent environmental issues for the target of local and global carbon neutrality.
This course provides students with fundamental knowledge of control systems. It covers the following topics: mathematical modelling and linear approximation of engineering systems, Laplace transform, transfer function and block diagram representation, characteristics of feedback systems, performance specifications, Routh-Hurwitz stability criterion, root locus design, frequency response design and Nyquist criterion. The utilization of computer-aided analysis and design software is also included.
The course is intended to enable students to learn the fundamentals of engineering design and how to carry out the design process. One (or several) engineering project(s)s for students to practice is (are) included with the following topics: engineering design process, innovation and design basics, CAD and CAE tools and applications, prototyping (mechanical workshop), prototyping (electronics workshop), quality and inspection.
This course will cover advanced topics in heat transfer and fluid mechanics including overview of macroscopic theory of heat transfer, microscopic picture of heat carriers and their transport, micro- and nanoscale energy transport in solids, chemical thermodynamics, chemical kinetics, multicomponent and multiphase mixtures, basic principles of computational fluid dynamics, turbulence modeling, and airflow simulation in enclosed environments.
This course introduces technologies, strategies as well as management and assessment systems to improve sustainability of buildings in relation to their environmental impacts. Applications such as passive design strategies, energy efficient systems, renewable energy and building information modelling are illustrated for enhancing the building performance and fulfilling green building assessment criteria and related regulations. The course will also enable students to adopt a lifecycle assessment approach to analyze building environmental performances and tackle with concurrent environmental issues for the target of local and global carbon neutrality.
This course presents an integrated introduction to the climate system, stressing the dynamics of the atmosphere and its physical and chemical interactions with the hydrosphere, biosphere and geosphere. The course applies basic scientific and mathematical principles to explain the history, current state and future projection of weather and climate, natural hazards (e.g., typhoons, floods), and global climate change in the context of natural variability and anthropogenic influence. Topics include Earth’s energy balance, climate feedback, convection and clouds, general circulation of the atmosphere and ocean, biogeochemistry and global carbon cycle, roles of vegetation and ecosystems, and historical and future climate change. Student taking this course are expected to have taken PHYS1111, CHEM1070 and MATH1010 or equivalent.
This course discusses from a multidisciplinary viewpoint the anthropogenic causes of environmental degradation and the various approaches to environmental protection and pollution control. Students are introduced the concept of sustainability in environmental protection, economic measures and voluntary approach in environmental management, control and treatment technologies, and their comparative effectiveness in the abatement of various types of pollution. Management programmes and control strategies in tackling local environmental problems are illustrated.
This course will cover a variety of topics related to air pollution science and engineering. Topics include: indoor and outdoor air quality (including particulate matters (PM) and gases pollutants); air pollution measurement and statistics; air quality meteorology and dispersion models; principles and challenges of air pollution control and measurement.
This course discusses the techniques and procedures of evaluating environmental consequences arising from human activities, with focus on their application in Hong Kong as prescribed under the Hong Kong Environmental Impact Assessment Ordinance, and its Technical Memorandum. Students are encouraged to take the laboratory course (ENSC4242) together with the lecture in order to have a better integration of theories and practical experiences on the subject.
This course examines the nature of noise, air and water pollution problems in cities and discusses how these pollutants and the provision of open/green space can affect urban livability. Particular emphasis is placed on the use of prediction models to assist environmental assessment and planning.
This course aims to offer students a broad exposure to the basic concepts and principles of hydrological science and thus to help them understand various technical and policy issues in water resources management. Focus is placed on all components of the hydrological cycle and the integration of hydrological processes for understanding runoff generation mechanisms at the hillslope and watershed scales. The concept and analysis of water balance are emphasized throughout the course. Principles and techniques of water resources management are also introduced, along with case studies in mainland China and Hong Kong.
The course introduces and examines the theories, processes and methodologies of environmental planning and assessment as important tools and instruments for minimizing human impacts on the environment and achieving environmental sustainability through good governance. Environmental planning plays a vital role in urban design and the formulation of land use and other planning strategies in order to mitigate the effects of human activities on air, water, land, and ecological systems, and to promote sustainable use of energy, water and other natural resources. While the coverage is broad and comprehensive, emphasis will be placed on the two most prominent tools, i.e. Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) and Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA), in terms of their origins, legal and regulatory requirements, and practices around the world. After introducing the conceptual framework and theoretical foundation of environmental assessment, specific methods and techniques (both qualitative and quantitative) will be introduced for students to understand the procedures and systems and gain the technical skills for practical applications. Environmental planning considerations and impact assessment will be examined for different sectors (industry, commercial, transportation, etc.) and multiple environmental media (air, water, solid waste, and noise) at difference spatial scales (local, regional, and national). Although a global perspective and comparative approach will be adopted throughout the course, examples and case studies of mitigating and managing environmental impacts through planning and assessment will mainly come from Hong Kong and mainland China.
Combustion and its control are essential to our daily life and more than 80% of the energy used nowadays is from combustion sources. This course starts with the basic principles that govern combustion phenomena such as conservation of mass, the first and second laws of thermodynamics, and the momentum principle. Then students will learn the new applications of these basic principles to account for the chemical transformations. We will discuss the basic concepts of chemical kinetics and the forms of reaction rate laws that apply in combustion processes, as well as mass transport phenomena. These laws will be applied to a variety of combustion phenomena, including spontaneous ignition of combustible mixtures, pollutant formation, internal combustion engine and fire safety.
This course focuses on a suite of materials characterization techniques that are useful in energy and environmental sciences. The main targets of these techniques include functional materials that are used in energy and environmental applications as well as solid, liquid, and gas samples that are involved in energy production and conversion, and pollution monitoring and control. The techniques include mass spectrometry (MS), gas chromatography (GC), high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), infrared (IR) spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), electron microscopy, and X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) spectroscopy. Students will receive lectures on the theory and operation principle of each technique as well as its limitations, and obtain hands-on experience with some of the techniques in supplemental lab sessions.
This is primarily for students in engineering faculty requiring a one-semester introductory in general chemistry at a fundamental level. It includes the study of atomic structure, bonding, periodic trends in physical properties, molecular geometry, stoichiometry, states of matter, thermodynamics, chemical equilibrium, acid/base chemistry, electrochemistry and kinetics.
This course aims to provide an intensive hands-on introduction to the C++ programming language. Topics include the basic C++ language syntax, variable declaration, basic operators, program flow and control, defining and using functions, file and operating system interface. Specific key features of the C++ programming language such as object-oriented methodology, class templates, encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, etc. will be highlighted.
This course aims to provide an intensive hands-on introduction to the Python scripting language. Topics include the basic Python language syntax, variable declaration, basic operators, programme flow and control, defining and using functions, file and operating system interface. Specific key features of the Python scripting language such as object-oriented support, functional programming support, lambda function, list comprehension, high level dynamic data types, embedding within applications, module creation etc. will be highlighted. Special topics include using Python for web/data access, animation, as well as using Python to develop a web crawler.
This course introduces the concept of abstract data types and the advantages of data abstraction. Various commonly used abstract data types including vector, list, stack, queue, tree, and set and their implementations using different data structures (array, pointer based structures, linked list, 2-3 tree, B-tree, etc.) will be discussed. Sample applications such as searching, sorting, etc., will also be used to illustrate the use of data abstraction in computer programming. Analysis of the performance of searching and sorting algorithms. Application of data structure principles.
This is a foundation course designed to equip students with a proper understanding of the fundamental aspects of environmental chemistry. It introduces the basic concept of chemical equilibrium and kinetics, the nature and characteristics of various common types of air and water pollution arising from industrial, agricultural and domestic sources. It outlines the principles of measurement for various parameters commonly used for air and water pollution studies, their significance and limitations. It also examines various types of aerial emission arising from combustion and industrial processes, and vehicles, and their chemical interaction leading to various global environmental issues such as the formation of photochemical smog, depletion of ozone layer and global warming effects.
This course introduces observations of and physical principles governing the circulation of the Earth’s atmosphere in relation to weather and climate. The topics covered include atmospheric composition and structure, convection, fundamentals of atmospheric motions, and the basic principles for weather and climate modeling. Physical principles covered include basic conservation laws, balanced flows, atmospheric thermodynamics, circulation and vorticity, atmospheric waves, and theories for various weather systems.
This course introduces the physical and chemical processes determining the composition for the atmosphere and its implications for climate, ecosystems, air pollution and human welfare. Topics covered include atmospheric structure, atmospheric chemistry models, atmospheric transport, chemical kinetics, stratospheric and tropospheric chemistry, chemistry of aerosols, biogeochemical cycles, as well as critical environmental issues including stratospheric ozone depletion, acid rain, photochemical smog, and climate change.
This course introduces the physical and chemical principles of hydrogeology. Concepts of surface and groundwater hydrology, as well as quantitative modelling of groundwater flow and contaminant transport are covered. Special topics on the coupling of hydrologic and geologic processes will also be addressed, with examples from tectonics, petroleum geology, geothermics, and global change.
This course introduces the physical, chemical and biological principles governing the functioning of terrestrial and marine ecosystems, and their roles in shaping the Earth’s climatic and geological environments. Topics include: basic hydrology and surface energy balance; energy, momentum, water and chemical exchange between ecosystems and the atmosphere; cycling of water, carbon and other nutrients in soil, vegetation and ocean; survival strategies of different life forms (especially plants and microorganisms); ecosystem structures and functions; landscapes, disturbances and ecosystem dynamics; human perturbations of biogeochemical cycles via pollution, greenhouse gas emissions and land use; responses and evolution of terrestrial and marine ecosystems under global climate change. This course serves as a comprehensive introduction to ecological climatology, biogeochemistry and ecosystem ecology, and requires basic mathematical operations.
This course includes the science behind the global warming issue, how the public views the issue and the critical thinking needed to analyze the evidence seen in the media/articles from the point of view of scientists. The world energy use, which is considered to be the cause of global warming, and the impacts are discussed in the course. In this course, students will learn about the radiation budgets/balance in the atmosphere, possible climate forcings that can upset the energy balance, how the earth’s global average temperature is measured, why global warming is described as “the biggest hoax” in human history, observations from the ocean and cryosphere and popular environmental issues/arguments discussed in the mainstream media. Newest observations from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) report are included throughout the course.
This course introduces the principles and applications of various chemical and physiochemical processes applicable for treatment and control of air and water pollution. It studies the processes of neutralization, oxidation-reduction, chemical precipitation, coagulation, flocculation, physical separation, absorption, adsorption, filtration, chemical disinfection, solvent extraction, fractional distillation and incineration. It also examines the applicabilities and limitations of such processes with reference to the treatment and recovery of toxic and hazardous chemical wastes. Site visits will be arranged to enhance students’ ability in application.
Remote sensing observations are critical for monitoring regional and global changes, determining spatial and temporal variability of the Earth System, and addressing fundamental global issues. This course introduces the basic physical principles of remote sensing, including electromagnetic waves and radiation, optical, microwave, and non-imaging remote sensing. It also presents key concepts and examples on remote sensing applications in Earth system science (such as atmosphere, lithosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere) and global changes. This course also provides computer-based lab exercises that facilitate the understanding of remote sensing principles and the processing of remote sensing data.
The objective of the course is to enable students to have a basic understanding of the practical aspects of the engineering profession. Prior to the enrolment of this course, students must have completed not less than 8 weeks of full-time internship approved by the Faculty of Engineering. To be qualified for award of the subject credit, the student must submit a report, within the semester of enrolment, summarizing what he or she has done and learnt during the internship, together with a testimonial from the corresponding employer. Pass or fail of the course will be determined by the professor-in-charge, based on the report and the testimonial submitted.
Student may look for internship opportunities at the Placement and Internship Program (PIP) website administered by Centre for Innovation and Technology of the Faculty, or from any other sources available to him or her. Students are recommended to seek professor-in-charge’s comment on internship undertaken before enrolling in the course.
Work-Study, the 12-month internship program organized by the Faculty, is a valid internship satisfying the requirements of ENGG1820.
Advisory: For year 2 or above Engineering Majors students. (new curriculum)
A first course in the fundamentals of probability theory and their applications in engineering. Topics include sample space and events, counting, axioms of probability, conditional probability, independence of events, discrete and continuous distributions, random variables, joint distributions, and limit theorems.
A first course in the fundamentals of statistics and their applications in engineering. Topics include populations and samples, point estimation, confidence intervals, hypothesis testing, and basics of linear regression.
The historical evolution of the human society is significantly affected by how we consume energy. Our modern society is built on modern energy consumption patterns. However, rising energy consumption also raises serious environmental challenges that are detrimental to human beings and our planet Earth. Accordingly, one critical goal of energy development is to maximize the positive impacts and to minimize the negative impacts of energy consumption. After discussing the role of energy consumption in a society, this course will analyze how energy consumption and the environment affect each other. Students will then be guided through various levels of a society, from individuals, households, communities, to cities, countries and the world in general discussion and case studies on how energy is consumed. Recognizing the importance of energy conservation as a key solution, this course will further examine two major barriers, particularly the behavior and efficiency gaps, to understand how we could achieve the goal. An open and especially active mind is a must for success in this course.
This course critically examines the interrelations between human activities and the environment, analyses the nature and roots of environmental problems, evaluates the effectiveness of various environmental management options and discusses the complexities of environmental policy-making.
This course introduces basic methods of resource evaluation and planning, giving special emphasis to cost-benefit analysis and economic policies for the management of natural resources. The course covers the different approaches developed by practitioners to give an economic value to environmental assets, discussing the theoretical underpinnings and methodological constraints of each approach, with examples from around the world. To strengthen understanding, the students are given the opportunity to carry out the economic evaluation of an environmental amenity in Hong Kong. The course also considers the problems of resource management, with a review of the methods developed by economists to encourage a more sustainable use of our natural resources.
Modern energy consumption and supply are a key foundation of our modern economy and society. After introducing energy consumption patterns and major influential factors, this course discusses major energy types, including coal, oil, natural gas, nuclear, hydro, wind, solar, biomass, and electricity from the perspectives of resources, production, technologies, policy, economic and social development. After taking the course, students will acquire comprehensive knowledge of various energy resources, their consumption and supply. Learning activities are designed to train students to think critically about the pros and cons of each energy type.
This course provides an introduction to the physical principles in meteorology, weather observation and forecasting. Topics include: physics of fluids; dynamic meteorology; atmospheric thermodynamics; atmospheric physics (cloud and lightning); weather systems and phenomena; weather observation, analysis and forecasting; climate change. Trips to Hong Kong Observatory headquarters/ outstations will be arranged to acquaint students with the operation of meteorological instruments and the real-life practice of weather analysis and forecasting. Students are advised to take PHYS3011 and 4011 before taking this course.
 Detailed Course List (2019-20 & thereafter)
Detailed Course List (2019-20 & thereafter)(For most updated course information, please view “Browse Program Information” at CUSIS or follow this path: AQS Homepage > Student Handbook > Course Details > Browse Course Catalog. Updated course information will be shown after July 1 every year.)
 Recommended Pattern of Study (2019-20 & thereafter)
Recommended Pattern of Study (2019-20 & thereafter) Programme Leaflet (Applicable to students admitted in 2025-26)
Programme Leaflet (Applicable to students admitted in 2025-26) Minor Programme Leaflet (Applicable to non-EEEN students)
Minor Programme Leaflet (Applicable to non-EEEN students)  Programme Website
Programme Website
